The ULA View
Most of the ZX Spectrum family of computers contains a ULA (Uncommitted Logic Array) chip, which renders the computer screen and I/O.
You can find this view in the Debug activity tag with the ULA & I/O header:
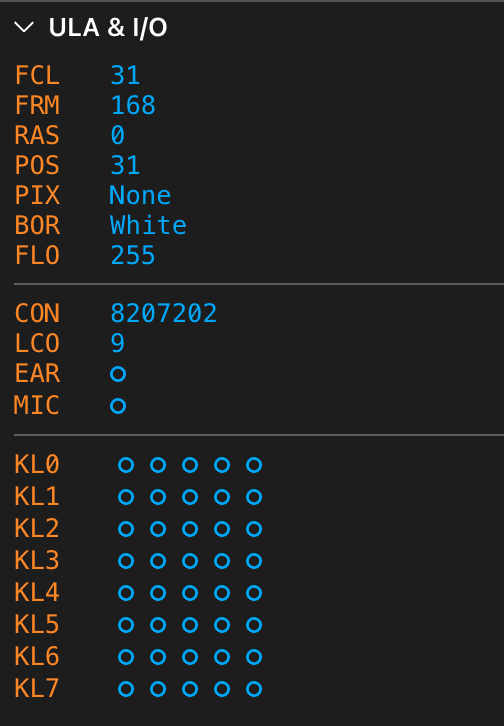
ULA Information
When you hover the mouse over the information item values, they display a tooltip naming the particular information on the display.
You can read this information in this panel:
FCL: Frame clock. This value shows the current screen rendering tact, which depends on the ZX Spectrum model. For example, the ZX Spectrum 48K (PAL) uses 69.888 tacts to render the entire screen, including the borders, blank area, and sync tacts.FRM: The number of frames rendered since the machine started.RAS: The raster line being renderedPOS: The current rendering position within the raster line.PIX: The current pixel rendering operation:None: A blank (non-visible) area is being rendered.Border: The ULA sets the border color to display the current pixel.BorderFetchPixel: The ULA sets the border color to display the current pixel. It prepares to display the first pixel in the row by pre-fetching the corresponding byte from the display memory.BorderFetchAttr: The ULA sets the border color to display the current pixel. It has already fetched the byte of eight pixels to display, and it prepares to display the first pixel in the row by pre-fetching the corresponding attribute byte from the display memory.DisplayB1: The ULA displays the subsequent two pixels of Byte1 sequentially during a single Z80 clock cycle.DisplayB2: The ULA displays the subsequent two pixels of Byte2 sequentially during a single Z80 clock cycle.DisplayB1FetchB2: The ULA displays the subsequent two pixels of Byte1 sequentially during a single Z80 clock cycle. It prepares to display the pixels of the next byte in the row by pre-fetching the corresponding byte from the display memory.DisplayB1FetchA2: The ULA displays the subsequent two pixels of Byte1 sequentially during a single Z80 clock cycle. It prepares to display the pixels of the next byte in the row by pre-fetching the corresponding attribute from the display memory.DisplayB2FetchB1: The ULA displays the subsequent two pixels of Byte2 sequentially during a single Z80 clock cycle. It prepares to display the pixels of the next byte in the row by pre-fetching the corresponding byte from the display memory.DisplayB2FetchA1: The ULA displays the subsequent two pixels of Byte2 sequentially during a single Z80 clock cycle. It prepares to display the pixels of the next byte in the row by pre-fetching the corresponding attribute from the display memory.
BOR: The current border color.FLO: The current floating bus value. This value is returned if the ZX Spectrum model reads an unhandled port at the current clock item.CON: The accumulated number of T-states spent because of memory access contention between the ULA and the CPU since the machine started.LCO: The accumulated number of T-states spent because of memory access contention between the ULA and the CPU since the machine was last paused.EAR: The EAR I/O bit (flag).MIC: The MIC I/O bit (flag).
Keyboard State
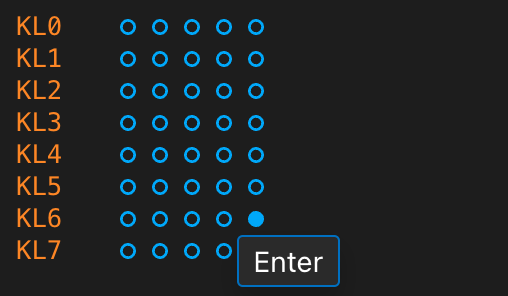
You can view the keyboard state, which is listed by the flags in the KL0, …, KL7 lines. Each flag represents a key’s state. The active value (filled circle) is for the pressed-down state. The tooltip shows the associated key’s name when you hover the mouse over a particular flag. For example, the following figure demonstrates that the rightmost flag in KL0 (the first key line) represents the Caps Shift key.
By clicking a particular key flag, you can toggle its state from pressed to released (and back). This feature is handy during debugging. After clicking the Enter key (the rightmost key in line 6), its state indicates that you have just toggled it.
The individual key lines represent these keyboard keys:
KL0:V,C,X,Z, andCaps Shift.KL1:G,F,D,S, andA.KL2:T,R,E,W, andQ.KL3:5,4,3,2, and1.KL4:6,7,8,9, and0.KL5:Y,U,I,O, andP.KL6:H,J,K,L, andEnter.KL7:B,N,M,Symbol Shift, andSpace.