The Watch View
With this view, you can observe values of symbols while developing and debugging. You can find this view in the Debug activity tab with the Watch header.
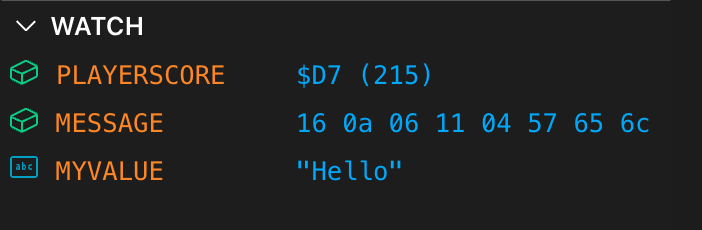
Each row represents a watch item with the following information:
- An icon showing the watch value category
- numeric (direct or indirect)
- string
- warning (when unresolved)
- The symbol name (uppercased)
- The current value (formatted)
When a watch cannot be evaluated yet (for example, compiled symbols or memory content are unavailable), it displays “<unknown>”. If the symbol is not found in the current compiled output, the value shows “<not found>”.
Note: To ensure symbol addresses are up to date, rebuild your project after making code changes. Unresolved symbols will display as “
<not found>”.
Adding and Removing Watch Items
You manage watches through interactive commands:
-
Add a watch
w-add [>]<symbol>[:<type>[:<length>]]>: optional; when present, uses the symbol’s direct value rather than reading from memory<type>:- b: 8-bit value
- w: 16-bit little-endian value
- -w: 16-bit big-endian value
- l: 32-bit little-endian value
- -l: 32-bit big-endian value
- f: flag (true/false)
- a: byte array (length required; default: 8 when omitted)
- s: string (length required; default: 8 when omitted)
-
Remove a watch
w-del <symbol> -
List watches
w-list -
Remove all watches
w-ea
In addition to commands, you can remove a watch directly in the Watch view by right‑clicking its icon.
Examples:
w-add playerScorew-add playerScore:ww-add >playerAddress:ww-add buffer:a:32w-add text:s:16
Understanding Value Formatting
The Watch panel formats values based on the symbol’s type and whether the watch is direct or memory-based.
-
Direct integer values (uses ’>’)
- Always shown as 16-bit number: $HHHH (D)
- Example: $12AB (4779)
-
Memory-based integer values (no ’>’)
- The symbol’s integer value is treated as a 16-bit address
- The panel reads memory according to the selected type and endianness
- Displayed as $HH (D), $HHHH (D), or $HHHHHHHH (D) for 8/16/32-bit types
-
Strings (type: s)
- Reads up to
<length>bytes, stops at NUL (0x00) - Non-printable bytes are shown as ’.’
- Displayed quoted: ”…”
- Reads up to
-
Arrays (type: a)
- Displays up to the first 16 bytes as hex pairs separated by spaces
- If longer than 16 bytes, shows a suffix like: … (+N)
-
Flags (type: f)
- Shown as true or false (non-zero => true)
Note: When you move the mouse over the watch item’s icon, the appearing tooltip will show the symbol’s display type.
Typical Workflows
-
Track a direct counter/constant
- w-add >frameCounter
- Shows as a 16-bit value regardless of the type
-
Monitor a pointer and the data it refers to
- w-add ptr:w # watch shows the 16-bit value at address ptr (little-endian)
- w-add textPtr:s:32 # shows a printable string at the location pointed by textPtr
-
Inspect a small memory block
- w-add buffer:a:16
Tips
- If you frequently work with strings or arrays and omit length, the default is 8.
- Use w-list to verify your watch specifications and types.
- Rebuild your project to update symbol addresses when you change code; unresolved symbols will display as “
<not found>”.